Nâng cao độ chính xác phân loại hoạt động của con người dựa trên các dấu hiệu micro-Doppler của radar FMCW bằng phương pháp ngưỡng
758 lượt xemDOI:
https://doi.org/10.54939/1859-1043.j.mst.95.2024.20-28Từ khóa:
Dấu hiệu micro-Doppler; Mạng nơron tích chập; Phân loại hoạt động người.Tóm tắt
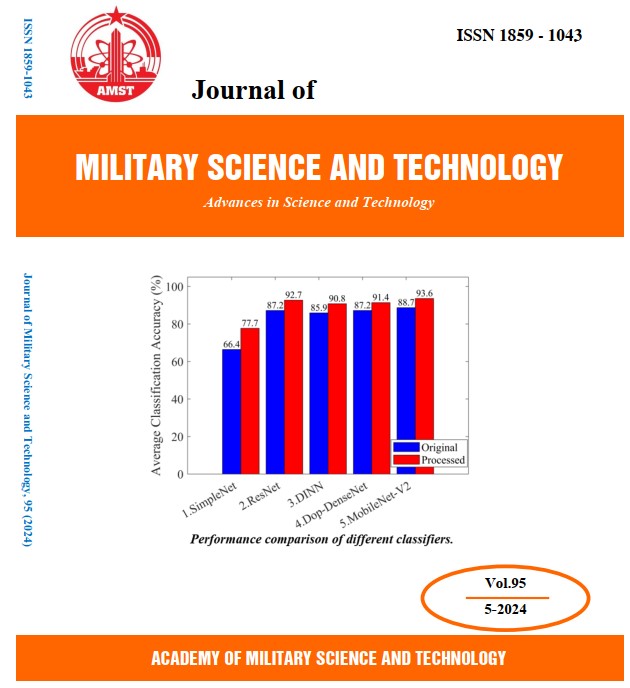
Ngày nay, phân loại hoạt động người dựa trên radar đang được ứng dụng rộng rãi trong các hệ thống chăm sóc sức khỏe dựa vào các ưu điểm về quyền riêng tư, không tiếp xúc và không bị ảnh hưởng bởi điều kiện thời tiết. Nghiên cứu này đề xuất một phương pháp ngưỡng được sử dụng trong giai đoạn tiền xử lý để cải thiện độ chính xác phân loại hoạt động người bằng cách xác định vùng thông tin có ý nghĩa (RMI) trên biểu đồ phổ. Ban đầu, một hàm mặt nạ, được tạo bởi một giá trị ngưỡng nhất định, được áp dụng cho biểu đồ phổ đầu vào để làm nổi bật RMI từ dấu hiệu micro-Doppler (m-D). Chỉ vùng RMI được đánh dấu trên biểu đồ phổ được giữ lại làm đầu vào cho các bộ phân loại. Sau đó, năm mạng nơron tích chập (CNNs) có độ phức tạp khác nhau được sử dụng để trích xuất các đặc trưng, phân loại hoạt động và đánh giá hiệu quả của phương pháp đề xuất. Kết quả thực nghiệm chứng minh rằng, phương pháp đề xuất đã nâng cao độ chính xác phân loại lên tới 11% khi so sánh với tập dữ liệu chưa được xử lý ban đầu.
Tài liệu tham khảo
[1]. H. Li, A. Shrestha, H. Heidari, J. Le Kernec, and F. Fioranelli, "Activities recognition and fall detection in continuous data streams using radar sensor," in 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), vol. 1, pp. 1-4, (2019).
[2]. J. Le Kernec et al., "Radar signal processing for sensing in assisted living: The challenges associated with real-time implementation of emerging algorithms," IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 29-41, (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2019.2903715
[3]. T. R. Bennett, J. Wu, N. Kehtarnavaz, and R. Jafari, "Inertial measurement unit-based wearable computers for assisted living applications: A signal processing perspective," IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 28-35, (2016). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2015.2499314
[4]. D. T. Nguyen, H. G. Hong, K. W. Kim, and K. R. Park, "Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras," Sensors, vol. 17, no. 3, p. 605, (2017). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030605
[5]. R. Igual, C. Medrano, and I. Plaza, "Challenges, issues and trends in fall detection systems," Biomedical engineering online, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 66, (2013). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-925X-12-66
[6]. V. C. Chen, F. Li, S.-S. Ho, and H. Wechsler, "Micro-Doppler effect in radar: phenomenon, model, and simulation study," IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and electronic systems, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 2-21, (2006). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402
[7]. Y. Kim and H. Ling, "Human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using a support vector machine," IEEE transactions on geoscience and remote sensing, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 1328-1337, (2009). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2009.2012849
[8]. H. Du, T. Jin, M. Li, Y. Song, and Y. Dai, "Detection of multi-people micro-motions based on range--velocity--time points," Electronics Letters, vol. 55, no. 23, pp. 1247-1249, (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2019.2419
[9]. X. Huang, J. Ding, D. Liang, and L. Wen, "Multi-person recognition using separated micro-Doppler signatures," IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 20, no. 12, pp. 6605-6611, (2020). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2977170
[10]. N. Nguyen, T. Nguyen, M. Pham, and Q. Tran, "Improving Human Activity Classification Based on Micro-Doppler Signatures Separation of FMCW Radar," in 2023 12th International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), pp. 454-459, (2023). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAIS59597.2023.10382332
[11]. S. A. Shah and F. Fioranelli, "Human activity recognition: Preliminary results for dataset portability using FMCW radar," in 2019 international radar conference (RADAR), pp. 1-4, (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/RADAR41533.2019.171307
[12]. F. A. Jibrin, A. Abdulaziz, A. S. Muhammad, A. D. Usman, and Y. Jibril, "Indoor Human Activity Classification Based on FMCW Radar Micro-Doppler Signatures and Deep-Learning Networks," in 2021 1st International Conference on Multidisciplinary Engineering and Applied Science (ICMEAS), pp. 1-5, (2021). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMEAS52683.2021.9692418
[13]. V. Winkler, "Range Doppler detection for automotive FMCW radars," in 2007 European Radar Conference, pp. 166-169, (2007). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/EURAD.2007.4404963
[14]. J. Allen, "Short term spectral analysis, synthesis, and modification by discrete Fourier transform," IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 235-238, (1977). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TASSP.1977.1162950
[15]. D. F. Fioranelli, D. S. A. Shah, H. Li1, A. Shrestha, D. S. Yang, and D. J. L. Kernec, "Radar sensing for healthcare: Associate editor francesco fioranelli on the applications of radar in monitoring vital signs and recognising human activity patterns," Electronics Letters, vol. 55, no. 19, pp. 1022-1024, (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2019.2378
[16]. K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, "Deep residual learning for image recognition," in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770-778, (2016).
[17]. N. Nguyen, M. Pham, V. Le, D. DuongQuoc, and V.-S. Doan, "Micro-Doppler signatures based human activity classification using Dense-Inception Neural Network," in 2022 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC), pp. 268-273, (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ATC55345.2022.9943046
[18]. H. Le, V.-P. Hoang, and others, "Dop-DenseNet: Densely Convolutional Neural Network-Based Gesture Recognition Using a Micro-Doppler Radar," Journal of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 335-343, (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.26866/jees.2022.3.r.95
[19]. M. Sandler, A. Howard, M. Zhu, A. Zhmoginov, and L.-C. Chen, "Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks," in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 4510-4520, (2018). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474